 It’s been 126 years since British medical doctor Sir Ronald Ross discovered that mosquitoes in the Anopheles family are primarily responsible for transmitting malaria parasites between vertebrate hosts.
It’s been 126 years since British medical doctor Sir Ronald Ross discovered that mosquitoes in the Anopheles family are primarily responsible for transmitting malaria parasites between vertebrate hosts.
Since his discovery, mosquitoes have been found to carry and transmit many other diseases that pose a major threat to public health. Among them are yellow fever, dengue and Zika.
Malaria is the most lethal mosquito-transmitted disease. The World Health Organisation reported an estimated 247 million cases of malaria worldwide in 2021 and 619 000 deaths. Almost all cases and deaths were in African countries.
Other diseases transmitted by mosquitoes are also a source of immense human suffering. It is estimated that dengue infects about 390 million people annually. And thousands are affected by Zika, chikungunya and yellow fever.
Insects that transmit diseases to humans are known as vectors and the diseases they transmit are referred to as vector-borne diseases. These diseases are very difficult to control. They generally have complex life cycles, involving both the insect and the human host.
Conventional methods to control vector-borne diseases have targeted the vectors, focusing on reducing their opportunities to come into contact with humans.
This is particularly true for malaria. Insecticide-treated nets serve a dual function by acting as a physical barrier between the mosquito vector and humans, and exposing the mosquito to a lethal dose of insecticide when it lands on the net. In another common control method, mosquitoes are exposed to a lethal dose of insecticide through indoor residual spraying.
Malaria burden
Both nets and indoor spraying have played a major role in reducing African countries’ malaria burden. But their sustained efficacy is under threat. Many vector populations have become resistant to the insecticides used in these methods. They have also changed their behaviours to reduce their contact with those insecticides.
Scientists are working to address these issues. But other methods that don’t rely on insecticides are needed in the fight against mosquito-borne diseases.
That’s where genetic modification comes in. We are researchers focused on finding novel ways to advance malaria elimination efforts and are excited about recent advances in genomic research that make genetic modification a realistic option for malaria control, in particular. As with other approaches to controlling or eventually eradicating the disease, this won’t be a complete solution. But it has the potential to strengthen the global fight against malaria.
Mosquitoes can be genetically modified through two different technologies. The first method, paratransgenesis, involves infecting mosquitoes with bacteria that prevent them from transmitting malaria. This doesn’t harm the mosquito. It is important not to eliminate or harm mosquitoes because they pollinate many plants and are food for animals like bats, birds and reptiles.
Scientists are excited about this method following the recent discovery of a bacterium that occurs naturally in mosquitoes’ guts and appears to prevent the malaria parasite from developing inside the mosquito.
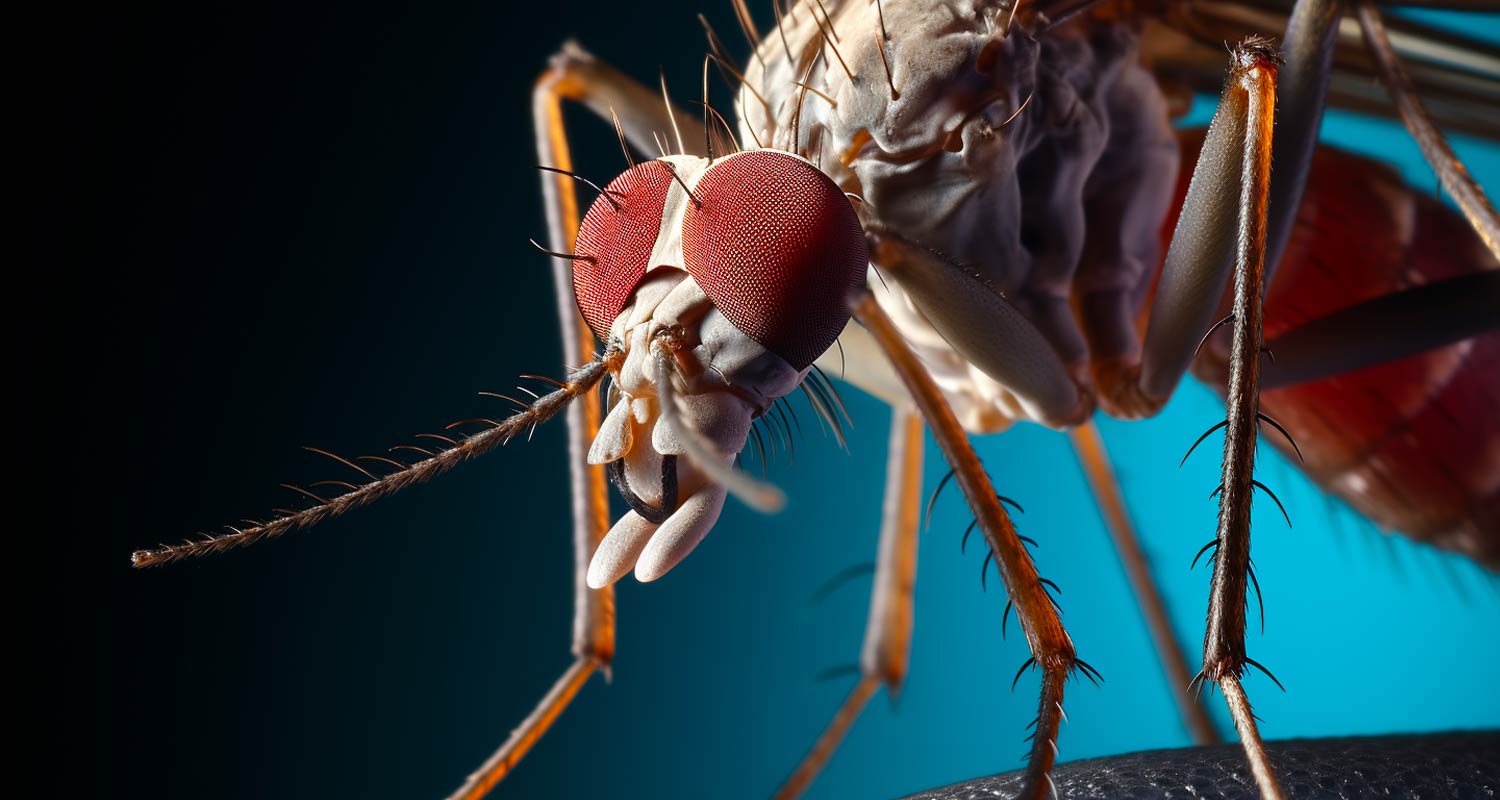 The second method involves genetically modifying the mosquitoes themselves. This approach centres on gene drives: genetic systems that ensure genes of interest are inherited by all offspring in every generation. There are two types of gene drive. One aims to reduce the vector population size and is known as population suppression. The other aims to prevent the mosquito from transmitting malaria; it is known as population modification.
The second method involves genetically modifying the mosquitoes themselves. This approach centres on gene drives: genetic systems that ensure genes of interest are inherited by all offspring in every generation. There are two types of gene drive. One aims to reduce the vector population size and is known as population suppression. The other aims to prevent the mosquito from transmitting malaria; it is known as population modification.
Gene drives focusing on population suppression have shown great promise in laboratory studies. They’ve yet to be tested in the field, though.
Population modification potentially has fewer environmental effects and is less prone to developing mutations. But it has proved more challenging to achieve and has not progressed as far as the suppression approach.
It will be a while before this technology is routinely used by malaria control programmes. But preparation is under way.
Over the past decade, malaria control programmes have expressed a willingness to use genetic modification if and when such techniques are shown to be safe and acceptable to the affected communities. This has prompted the World Health Organisation to provide guidance on the use of genetically modified mosquitoes to control malaria and other vector-borne diseases.
It is critical that the concerns of communities where genetically modified mosquitoes are to be released are addressed prior to any release
In its guidance, the WHO acknowledges how crucial community engagement will be to the success of any future gene drive interventions.
This is important in an environment where there is marked scepticism about science, and particularly about genetically modified organisms (GMOs). In 2003, community resistance resulted in the rejection of genetically modified golden rice in Zambia, despite the country experiencing a pronounced food shortage.
More recently, there was backlash against the Covid-19 mRNA vaccines, which some people suspected of being capable of altering human DNA (it isn’t).
It is critical that the concerns of communities where genetically modified mosquitoes are to be released are addressed prior to any release. This will help promote acceptance and understanding of the new technology.
However, community acceptance is not the only challenge. There is an urgent need for research on the relevant local malaria mosquito species so that the required genetically modified mosquitoes can be developed. Once the genetically modified lines are established, impact in the field must be demonstrated and systems established to ensure suitable numbers of mosquitoes can be reared and safely transported to the intervention sites.
 All this requires considerable human resources and funding, suggesting that it will be some time before gene drive systems have real-world impact on malaria transmission.
All this requires considerable human resources and funding, suggesting that it will be some time before gene drive systems have real-world impact on malaria transmission.
Still, as the globe marks World Mosquito Day on 20 August, in honour of Sir Ronald Ross’s discovery almost 130 years ago, we believe there is reason for optimism: novel technologies like genetic modification have the potential to play a major role in the fight against malaria.![]()
- The authors are Shüné Oliver, medical scientist, South African National Institute for Communicable Diseases, and Jaishree Raman, principal medical scientist and head of laboratory for antimalarial resistance monitoring and malaria operational research, also at the institute
- This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons licence

