
The demand for cheaper, greener electricity means that the energy landscape is changing faster than at any other point in history. This is particularly true of solar-powered electricity and battery storage. The cost of both has dropped at unprecedented rates over the past decade and energy-efficient technologies such as LED lighting have also expanded.
Access to cheap and ubiquitous solar power and storage will transform the way we produce and use power, allowing electrification of the transport sector. There is potential for new chemical-based economies in which we store renewable energy as fuels, and support new devices making up an “Internet of things”.
But our current energy technologies won’t lead us to this future: We will soon hit efficiency and cost limits. The potential for future reductions in the cost of electricity from silicon solar, for example, is limited. The manufacture of each panel demands a fair amount of energy and factories are expensive to build. And although the cost of production can be squeezed a little further, the costs of a solar installation are now dominated by the extras – installation, wiring, the electronics and so on.
This means that current solar power systems are unlikely to meet the required fraction of our 30 terawatt global power requirements (they produce less than 1TW today) fast enough to address issues such as climate change.
Likewise, our current LED lighting and display technologies are too expensive and not of good enough colour quality to realistically replace traditional lighting in a short enough time frame. This is a problem, as lighting currently accounts for 5% of the world’s carbon emissions. New technologies are needed to fill this gap, and quickly.
Our lab in Cambridge, England is working with a promising new family of materials known as halide perovskites. They are semiconductors, conducting charges when stimulated with light. Perovskite inks are deposited onto glass or plastic to make extremely thin films — around one hundredth of the width of a human hair — made up of metal, halide and organic ions. When sandwiched between electrode contacts, these films make solar cell or LED devices.
Versatile
Amazingly, the colour of light they absorb or emit can be changed simply by tweaking their chemical structure. By changing the way we grow them, we can tailor them to be more suitable for absorbing light (for a solar panel) or emitting light (for an LED). This allows us to make different colour solar cells and LEDs emitting light from the ultraviolet, right through to the visible and near-infrared.
Despite their cheap and versatile processing, these materials have been shown to be remarkably efficient as both solar cells and light emitters. Perovskite solar cells hit 25.2% efficiency in 2019, hot on the heels of crystalline silicon cells at 26.7%, and perovskite LEDs are already approaching off-the-shelf organic light-emitting diode (OLED) performances.
These technologies are rapidly being commercialised, particularly on the solar cell front. UK-based Oxford Photovoltaics has built a production line and is filling its first purchase orders in early 2021. Polish company Saule Technologies released prototype products at the end of 2018, including a perovskite solar façade pilot. Chinese manufacturer Microquanta Semiconductor expects to produce more than 200 000 square metres of panels in its production line before yearend. The US-based Swift Solar (a company I co-founded) is pioneering high-performance cells with lightweight, flexible properties.
Between these and other companies, there is rapid progress being made.
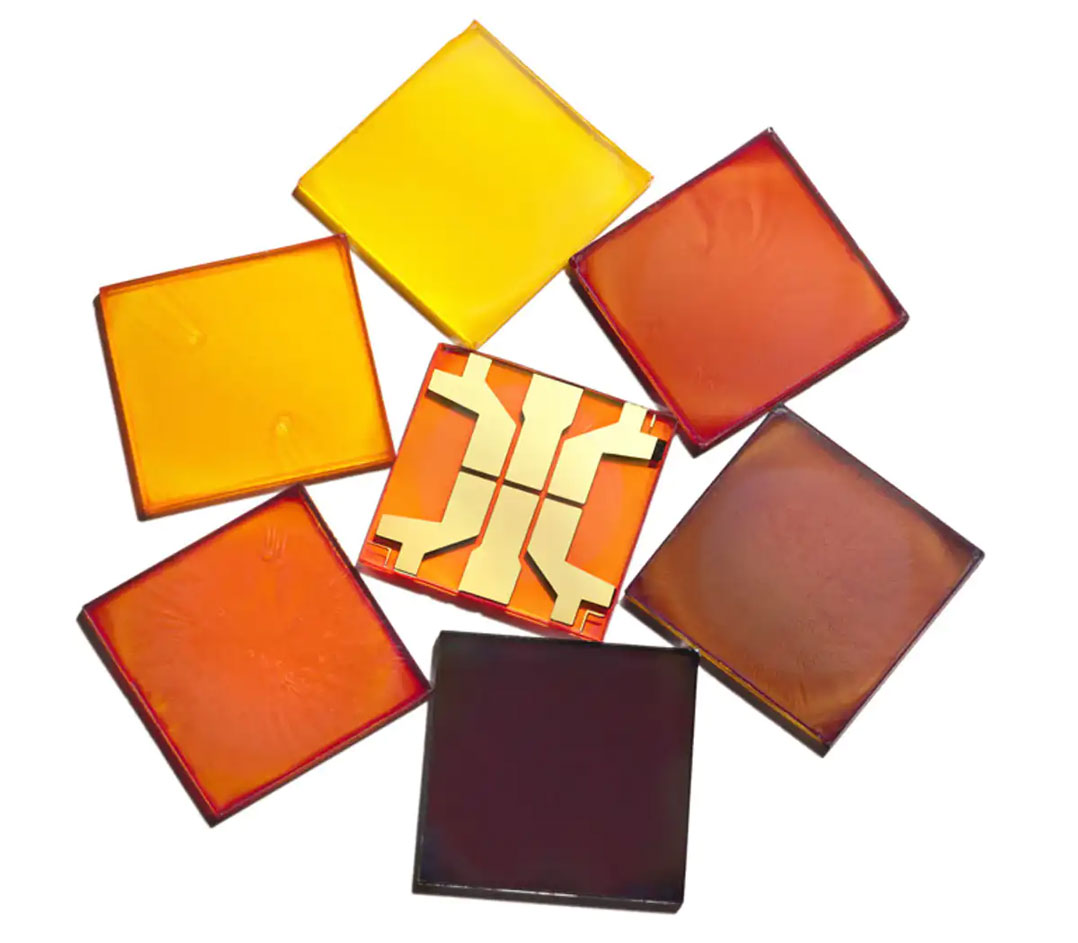
Unlike conventional silicon cells, which need to be very uniform for high efficiency, perovskite films are comprised of mosaic “grains” of highly variable size (from nanometres to millimetres) and chemistry — and yet they perform nearly as well as the best silicon cells today. What’s more, small blemishes or defects in perovskite films do not lead to significant power losses. Such defects would be catastrophic for a silicon panel or a commercial LED. Although we are still trying to understand this, these materials are forcing the community to rewrite the textbook for what we consider as an ideal semiconductor: They can have very good optical and electronic properties in spite of — or perhaps even because of — disorder.
We could hypothetically use these materials to make “designer” coloured solar cells that blend in to buildings or houses, or solar windows that look like tinted glass yet generate power.
But the real opportunity is to develop highly efficient cells beyond the efficiency of silicon cells. For example, we can layer two different coloured perovskite films together in a “tandem” solar cell. Each layer would harvest different regions of the solar spectrum, increasing the overall efficiency of the cell.
Efficiency boost
Another example is what Oxford PV are pioneering: adding a perovskite layer on top of a standard silicon cell, boosting the efficiency of the existing technology without significant additional cost. These tandem layering approaches could quickly create a boost in efficiency of solar panels beyond 30%, which would reduce both the panel and system costs while also reducing their energy footprint.
These perovskite layers are also being developed to manufacture flexible solar panels that can be processed to roll like newsprint, further reducing costs. Lightweight, high-power solar also opens up possibilities for powering electric vehicles and communication satellites.
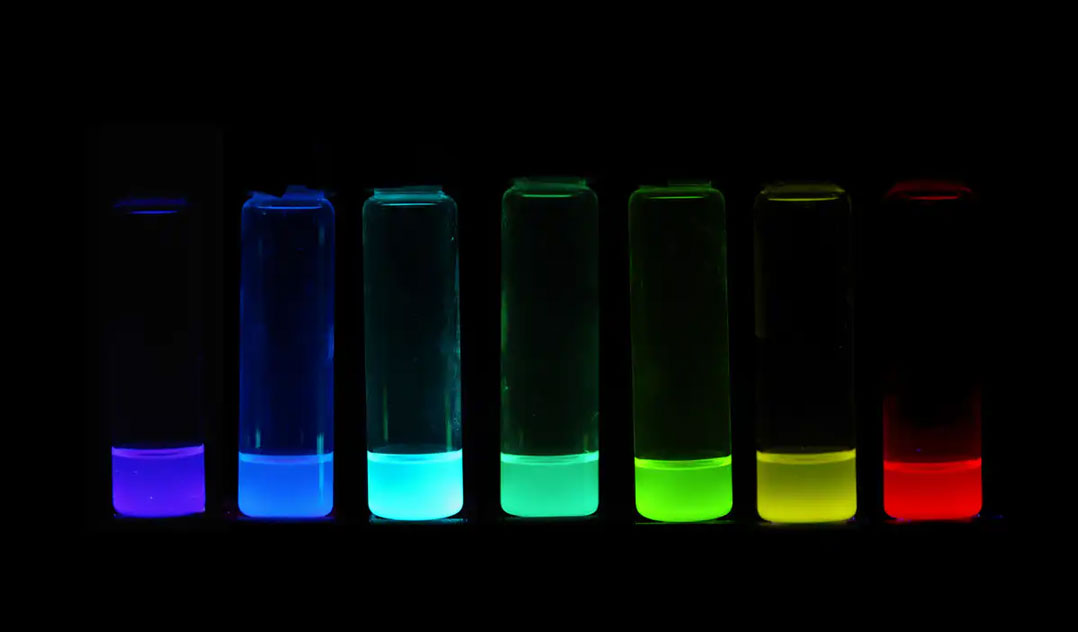

For LEDs, perovskites can achieve fantastic colour quality which could lead to advanced flexible display technologies. Perovskites could also give cheaper, higher quality white lighting than today’s commercial LEDs, with the “colour temperature” of a globe able to be manufactured to give cool or warm white light or any desired shade in between. They are also generating excitement as building blocks for future quantum computers, as well as X-Ray detectors for extremely low dose medical and security imaging.
Although the first products are already emerging, there are still challenges. One key issue is demonstrating long-term stability. But the research is promising, and once these are resolved, halide perovskites could truly propel the transformation of our energy production and consumption.![]()
- Written by Sam Stranks, lecturer in energy and Royal Society University research fellow, University of Cambridge
- This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons licence




