
MTN has been running a long-term evolution (LTE) trial in recent weeks in parts of Johannesburg and Pretoria. TechCentral’s Craig Wilson put the network through its paces and was suitably impressed.
LTE is a mobile broadband system that some network operators in the US refer to, somewhat contentionally, as fourth-generation technology. It’s seen as the successor technology to the high-speed packet access networks currently employed by all four of SA cellular providers. The new technology promises theoretical speeds of up to 100Mbit/s — and much faster speeds in future.
In order to run the pilot network, MTN has reallocated (“refarmed”, in industry parlance) part of its 1,8GHz spectrum allocation. MTN SA MD Karel Pienaar has said the company would like to build the network at 800MHz and 2,6GHz, but the allocation of these bands of spectrum has yet to happen.
MTN is strongly rumoured to be in talks with iBurst parent Wireless Business Solutions about gaining access to the latter’s allocation in the 1,8GHz band to help facilitate its LTE plans. An iBurst executive said on Thursday the company was being courted by “suitors”.
The network is available in selected parts of Gauteng, in areas where it’s built fibre to its base stations.
The Independent Communications Authority of SA is expected to auction off access to 2,6GHz later this year, but the 800MHz band, which is far more desirable for outlying areas, may only follow once SA’s television broadcasters switch to digital transmission.
MTN appears to be eager to deploy LTE as fast as possible. Doing so could give it a competitive advantage should it get it to market before its rivals.
To test the pilot network, TechCentral ran three speed tests each to facilities in Johannesburg, London and New York. The tests were conducted around the Sandton CBD. The results varied greatly. New York, for example offered download speeds as high at 17,09Mbit/s in one test and a 5,33Mbit/s in another.
Tests to the MTN Business data centre in Johannesburg showed similarly wide variances, but always returned double-digit download speeds with ping times (the round trip time for data) in the region of 25ms to 30ms, which is exceptional for a cellular network.
Screenshots of the best result from each of the three cities tested follow below.
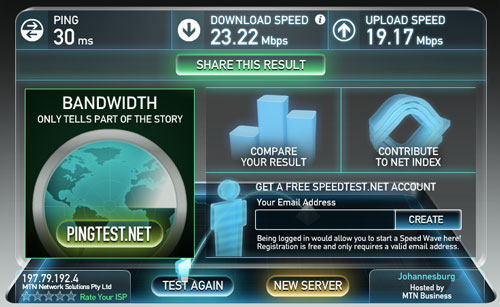

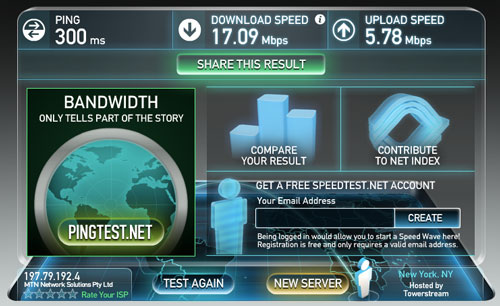
TechCentral conducted its tests using a Huawei E398 LTE USB rotator dongle, which is considerably larger than the average 3G dongle, meaning we had to either use a USB extension cord or sacrifice one of the two USB ports on the MacBook we used to test it.
The biggest concern was the rate at which the dongle devours battery power. Within 10 minutes of use, the MacBook’s battery had dropped by 10%.
The big question, of course, is how well the LTE service will perform once it’s launched commercially and users start putting load on the system. — Craig Wilson, TechCentral
- Subscribe to our free daily newsletter
- Follow us on Twitter or on Facebook
- Visit our sister website, SportsCentral (still in beta)




