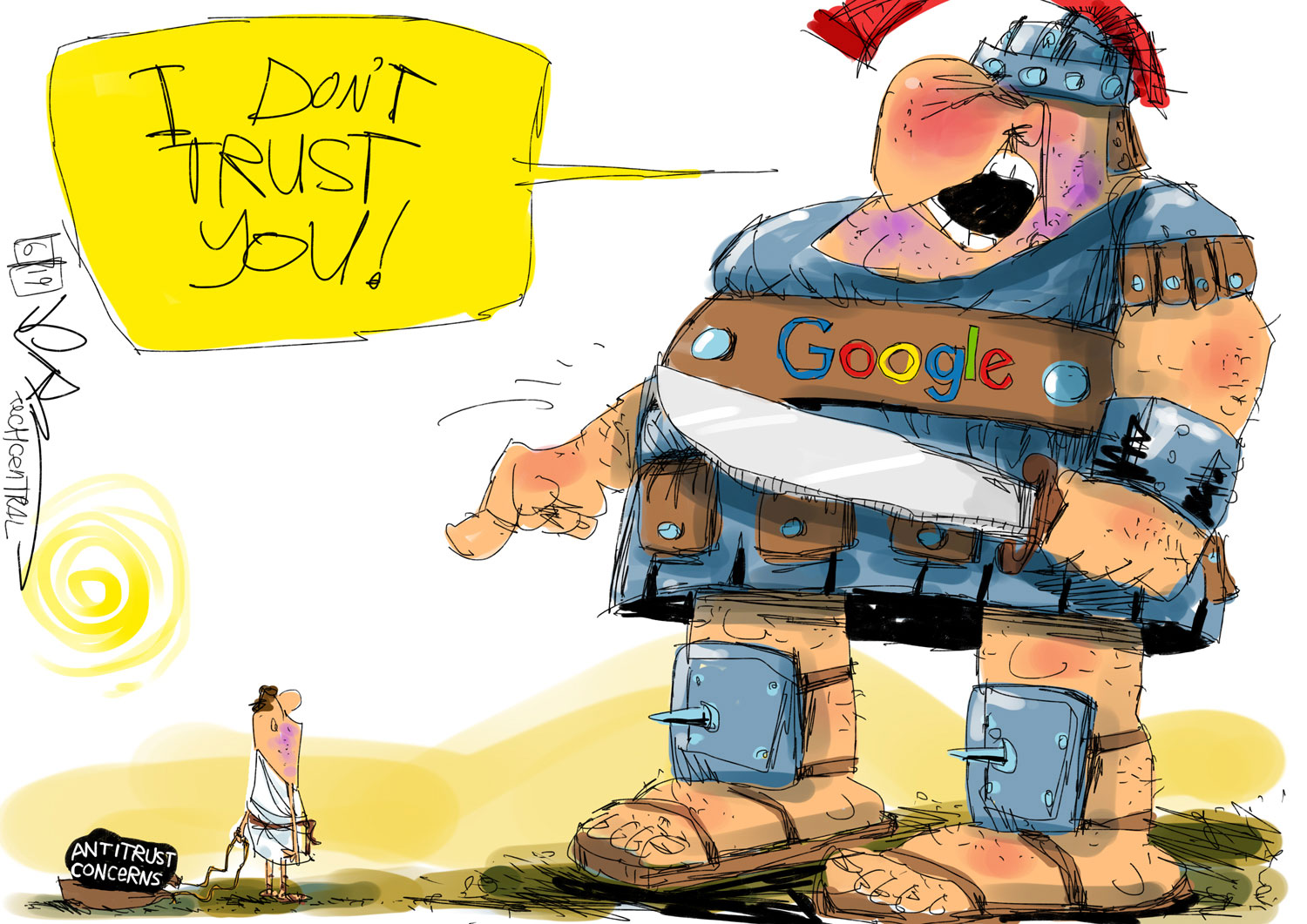
 As the public and government regulators around the world discuss whether and how to manage the power of technology companies, one idea that keeps coming up is breaking up these large conglomerate corporations into smaller pieces. Public distrust for tech companies has shifted to talk of antitrust action against them. Facebook, for instance, might then have to compete with Instagram for photo-sharing and WhatsApp for messaging — rather than owning both.
As the public and government regulators around the world discuss whether and how to manage the power of technology companies, one idea that keeps coming up is breaking up these large conglomerate corporations into smaller pieces. Public distrust for tech companies has shifted to talk of antitrust action against them. Facebook, for instance, might then have to compete with Instagram for photo-sharing and WhatsApp for messaging — rather than owning both.
The idea has managed to garner support from both Massachusetts senator Elizabeth Warren, a Democrat, and Republican President Donald Trump.
However, advocates and opponents of breaking up big technology firms are falling prey to some serious misconceptions. I study the effects of digital technologies on lives and livelihoods across 85 countries and lead Tufts Fletcher School’s Digital Planet initiative studying technological innovation around the world. In my opinion, there are three myths worth busting before considering taking on big tech.
Myth 1: Comparing Standard Oil and Google
Arguments for and against antitrust action against tech firms rely heavily on the experiences of earlier cases. The massive 19th-century monopoly Standard Oil has, in fact, been referred to as the “Google of its day”. There are also people who are recalling the 1990s antitrust case against Microsoft’s dominant position in the era of personal computers.
Those cases from the past may seem similar to today’s situation, but this era is different in one crucial way: the global technology marketplace. Currently, there are two parallel “big tech” clusters. One is in the US, dominated by Google, Amazon, Facebook and Apple. The other is based in China, dominated by Baidu, Alibaba, Tencent and Huawei. This global market is subject to different political and policy pressures than regulators faced when dealing with Standard Oil and Microsoft.
 Both clusters are attempting to add users to accumulate reservoirs of data, which will fuel the next stage of competitiveness in a future run by artificial intelligence. The Chinese government has blocked most of the US companies from entering the Chinese market, protecting its “AI national team”. The US government has done likewise, blacklisting some Chinese outfits for a period while discouraging others.
Both clusters are attempting to add users to accumulate reservoirs of data, which will fuel the next stage of competitiveness in a future run by artificial intelligence. The Chinese government has blocked most of the US companies from entering the Chinese market, protecting its “AI national team”. The US government has done likewise, blacklisting some Chinese outfits for a period while discouraging others.
If the US technology giants are broken up, the result would be a vastly uneven global playing field, pitting fragmented US companies against consolidated state-protected Chinese firms.
Geopolitical factors aren’t limited to the US-China rivalry. The European Union, Russia and India are also heavy users of Silicon Valley technologies, and each is exploring its own options for legislation and regulation, too.
US companies’ size and data accumulation capabilities give the country economic and political influence around the globe. Their power would change if they were broken up — and that should be a key consideration in regulators’ decisions.
Myth 2: Price is right
There are two main views of antitrust action in these discussions. One focuses on consumer welfare, which has been the prevailing approach federal lawyers have taken since the 1960s. The other view suggests that regulators should look at the underlying structure of the market and potential for powerful players to exploit their positions.
Those two sides seem to agree that price plays a key role. People who argue against breaking up the tech giants point out that Facebook and Google provide services that are free to the consumer, and that Amazon’s marketplace power drives its products’ costs down. On the other side, though, are those who say that having low or no prices is evidence that these companies are artificially lowering consumer costs to draw users into company-controlled systems that are hard to leave.
Both sides are missing the fact that the monetary price is less relevant as a measure of what users pay in the technology industry than it is in other types of business. Users pay for digital products with their data, rather than just money. Regulators shouldn’t focus only on the monetary costs to the users. Rather, they should ask whether users are being asked for more data than is strictly necessary, whether information is being collected in intrusive or abusive ways and whether customers are getting good value in exchange for their data.
Myth 3: Trust-busting is all or nothing
There aren’t just two ways for this debate to end, with either a breakup of one or more technology giants or simply leaving things as they are for the market to develop further.
The best outcome would take a page from the history of antitrust litigation: the company that is sued is not broken up, and yet the very fact that there was a lawsuit leads to progress. That has happened in the past, in the cases against the Bell System, IBM and Microsoft.
In the 1956 federal consent decree against the Bell System, which settled a seven-year legal proceeding against the company, the company wasn’t split up, but Bell was required to license all its patents royalty-free to other firms. This meant that some of the most profound technological innovations in history — including the transistor, the solar cell and the laser — became widely available, yielding computers, solar power and other technologies that are crucial to the modern world. When the Bell System was eventually broken up in 1982, it did not do nearly as much to spread innovation and competition as the agreement that kept the Bells together a quarter of a century earlier.
The antitrust action against IBM lasted 13 years and didn’t break up the firm. However, as part of its tactics to avoid appearing to be a monopoly, IBM agreed to separate pricing for its hardware and software products, previously sold as an indivisible bundle. This created an opportunity for entrepreneurs Bill Gates and Paul Allen to create a new software-only company, called Microsoft. The surge of software innovations that have followed can clearly trace their origins to the IBM settlement.
 Two decades later, Microsoft was itself the target of an antitrust action. In the resulting settlement, Microsoft agreed to ensure its products were compatible with competitors’ software. That made room in the emerging Internet marketplace for Web browsers, the predecessors of Apple’s Safari, Mozilla’s Firefox and Google Chrome.
Two decades later, Microsoft was itself the target of an antitrust action. In the resulting settlement, Microsoft agreed to ensure its products were compatible with competitors’ software. That made room in the emerging Internet marketplace for Web browsers, the predecessors of Apple’s Safari, Mozilla’s Firefox and Google Chrome.
Even Margrethe Vestager, the European Union’s top antitrust official and frequent tech-giant nemesis, has said that “antitrust prosecutions are part of how technology grows”. But that doesn’t mean they all have to achieve their most extreme ends, of breaking up the companies.
Antitrust rules are complicated enough, and plenty of experts will be called on to give their views on what to do with “Big Tech”. Technology pervades every aspect of modern lives, giving each person a responsibility to weigh in on this issue without misconceptions clouding their judgments. Technology has become a political issue. In a politically overheated climate, public sentiments may matter even more than the opinions of experts.![]()
- Written by Bhaskar Chakravorti, dean of Global Business, The Fletcher School, Tufts University
- This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons licence